Creating Perfect Audio Spectrum Effect in After Effects
Visualizing music is an engaging way to represent audio graphically. In this guide, I’ll introduce an alternative method to create audio spectrum effects, focusing on triangular shapes. This technique offers a unique way to visualize music, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of your audio representation.
Preparing the Workspace
To begin, you’ll need a music track, which can be sourced from platforms like YouTube’s sound library. Create a new composition in your video editing software, setting it to a 30-second duration with a 1920x1080px resolution and a black background. Drag your chosen audio file into the sequence and press ‘L’ on your keyboard to enable the sound wave feature. When you preview the track, you’ll observe the sound waves and their corresponding tones.
Creating the Visual Elements
Start by creating a new solid layer, which will serve as the foundation for the audio spectrum effect. Right-click on the sequence, choose ‘New’, then ‘Solid’, and make sure it matches the size of your composition.
Interestingly, you can’t draw a triangle directly in most editing software. Instead, use the rectangle tool to draw a square and then use the Pen Tool with the Delete Vertex Tool to remove a point, forming a triangle. To ensure it’s a downward-facing triangle, use the selection tool to adjust its orientation.
Utilize the Align panel to center the triangle in your composition. In the effects section, search for ‘Audio Spectrum’ and apply it to your solid layer. Initially, you won’t see any changes until you link the audio spectrum effect to your music file. Change the audio layer option in the effects controls panel to your music file.
Refining the Audio Spectrum Effect
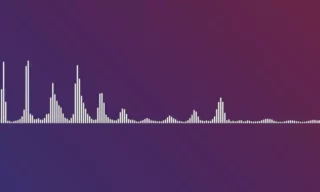
Adjust the start frequency to 1 and the end frequency to around 500 for optimal visualization. Increase the frequency bands to around 100 for a more detailed appearance. You can also adjust the thickness of the spectrum lines as per your preference.
Set the color to white for clarity, though you have the option to change it later. The Side Options value is crucial; ‘A’ displays the spectrum effect on one side, ‘B’ on the other, and selecting both showcases the effect on both sides.
Duplicate the audio spectrum layer and experiment with various display options like ‘Analog Lines’ and ‘Analog Dots’. Adjust settings like the maximum height and thickness to customize the appearance. Utilize the ‘Composite on Original’ option to layer these effects without overlap.
Enhancing the Visual Appeal
Apply a mirror effect to the audio spectrum layer and adjust the center point to align with the middle of your project. This creates a symmetrical visual effect.
Create a new solid layer for the background and apply a ‘Starburst’ effect. Adjust the speed and grid settings to create a dynamic background. Adding a ‘Radial Fast Blur’ can further enhance the visual complexity.
Apply a glow effect to the audio spectrum layers, adjusting the threshold, radius, and intensity for a glowing appearance. Add an adjustment layer for color correction, using curves to create a vibrant and dynamic color scheme. Switching the project settings from 8 bits to 16 bits can make the colors more vivid.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey from audio waves to striking visual spectacles is both fascinating and creatively fulfilling. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can transform any piece of music into a visual feast of colors, shapes, and movements.